On this page
The Act makes it illegal to harm Aboriginal cultural heritage unless a relevant approval has been obtained.
Protecting cultural heritage
Key decision makers in the Aboriginal cultural heritage system
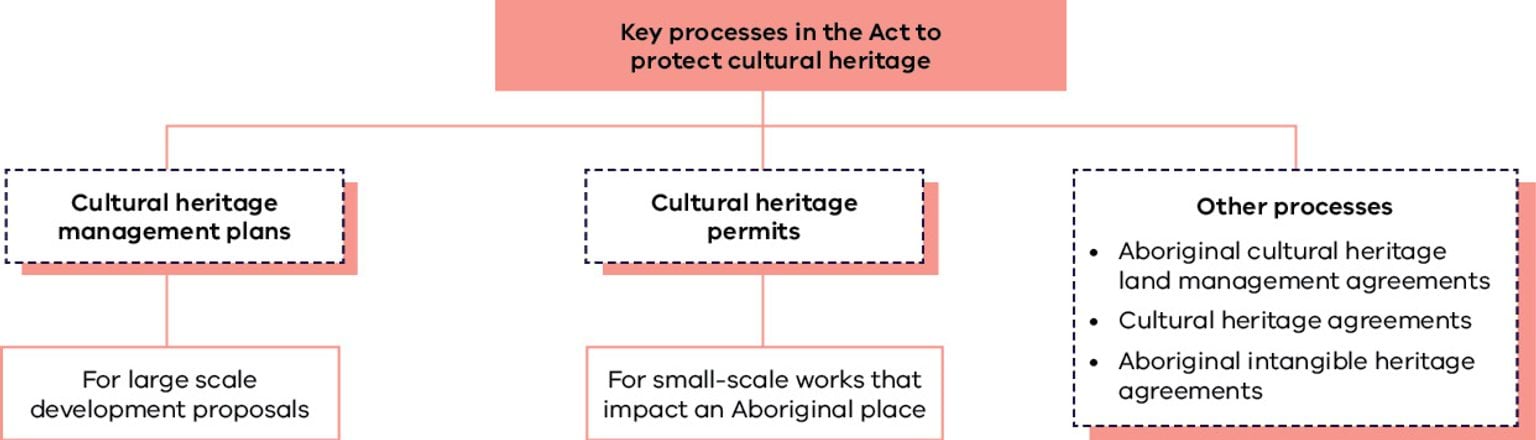
For large scale development proposals
A cultural heritage management plan (CHMP) includes a regulated assessment of the impact of a proposed land use activity on Aboriginal cultural heritage values.
A CHMP is required when a ‘high impact activity’ is planned for an ‘area of cultural heritage sensitivity’.
The CHMP provides an expert report outlining measures a sponsor must take to manage and protect Aboriginal cultural heritage before, during and after a proposed activity.
Generally, a CHMP is not required in areas that have already been heavily developed. This is because the ‘significant ground disturbance’ from the previous development means an area is no longer an ‘area of cultural heritage sensitivity’
High impact activity
Generally includes larger scale buildings and works that will cause or result in ‘significant ground disturbance’.
For example:
- the construction of three or more dwellings
- subdivisions of three or more lots
- mining and quarrying
- new roads and infrastructure.
For a comprehensive list see part 2, division 5 in the Regulations.
Areas of cultural heritage sensitivity
These include:
- registered Aboriginal places
- waterways, ancient lakes and Ramsar wetlands
- Coastal land, dunes and caves
These areas are mapped on Aboriginal Victoria's Aboriginal Cultural Heritage Register and Information System.
Significant ground disturbance
Disturbance of the topsoil or surface rock layer of the ground or a waterway by machinery in the course of grading, excavating, digging, dredging or deep ripping.
For small-scale works that impact an Aboriginal place
Several actions are controlled under the Act. Permits may be obtained for these actions.
If your proposed project requires a cultural heritage management plan (CHMP), you cannot get a permit for the activity.
Controlled or unlawful activities include:
- harming an Aboriginal place
- selling an Aboriginal object that was not made for sale
- removing an Aboriginal object from Victoria
- disturbing or excavating land to uncover or discover Aboriginal cultural heritage
- carrying out research on an Aboriginal place or object
Read about cultural heritage permits.
Aboriginal cultural heritage land management agreements
Aimed at public land managers to manage their responsibilities over large areas of land.
Read about Aboriginal cultural heritage land management agreements.
Cultural heritage agreements
For private landowners to protect Aboriginal cultural heritage on their properties.
Read about cultural heritage agreements.
Aboriginal intangible heritage agreements
For commercial use and development of registered traditional knowledge.
Read about Aboriginal intangible heritage.
Updated